智能指针,是安卓为了照顾Java层代码,为C层适配的一种自动管理内存对象的方案。由于C层对象不能够像Java层代码一样由虚拟机自动释放,很容易造成内存泄漏等问题,其生命周期要求开发者自行管理,为了解决这个问题,安卓系统便引入了智能指针的概念。在我们了解它之后,对于源码的阅读,无疑将会变得更加轻松!
概述
- 智能指针能够通过引用计数来维护对象的生命周期
- 智能指针是一个对象,而不是一个指针
- 智能指针构造时,增加它引用对象的引用计数,析构时,减少引用对象的引用计数
- 对象的生命周期只受强引用计数控制,不受弱引用计数控制
- “父” 对象通过强引用计数引用 “子” 对象,“子” 对象通过弱引用计数引用 “父” 对象
- 轻量级指针,强指针,弱指针
LightRefBase
LightRefBase轻量级指针
RefBase
如果一个类支持使用轻量级指针,那么就必须继承LightRefBase,其源码如下
–> /system/core/include/utils/RefBase.h
template <class T>
class LightRefBase
{
public:
// 引用计数值,初始化值0
inline LightRefBase() : mCount(0) { }
// 增加引用计数
inline void incStrong(__attribute__((unused)) const void* id) const {
android_atomic_inc(&mCount);
}
// 减少引用计数
inline void decStrong(__attribute__((unused)) const void* id) const {
// 根据减少引用计数之前的值,判断是否释放相应内存
if (android_atomic_dec(&mCount) == 1) {
delete static_cast<const T*>(this);
}
}
//! DEBUGGING ONLY: Get current strong ref count.
inline int32_t getStrongCount() const {
return mCount;
}
typedef LightRefBase<T> basetype;
protected:
inline ~LightRefBase() { }
private:
friend class ReferenceMover;
inline static void renameRefs(size_t n, const ReferenceRenamer& renamer) { }
inline static void renameRefId(T* ref,
const void* old_id, const void* new_id) { }
private:
mutable volatile int32_t mCount;
};
LightRefBase是一个模版类,T代表的是实际的类型,继承LightRefBase
- 基类初始化时,内部的mCount为0,用来描述引用计数值
- 通过incStrong()实现引用计数的增加,decStrong()减少引用计数
- 在引用计数为0时,需要删除对象,释放内存
LightRefBase实现类
轻量级指针的实现类为StrongPointer,同时也是强指针的实现类。
–> /system/core/include/utils/StrongPointer.h
template<typename T>
class sp {
public:
// m_ptr指向实际引用的对象
inline sp() : m_ptr(0) { }
// 四种构造函数
sp(T* other);
sp(const sp<T>& other);
template<typename U> sp(U* other);
template<typename U> sp(const sp<U>& other);
~sp();
// 运算操作符重载
sp& operator = (T* other);
sp& operator = (const sp<T>& other);
template<typename U> sp& operator = (const sp<U>& other);
template<typename U> sp& operator = (U* other);
//! Special optimization for use by ProcessState (and nobody else).
void force_set(T* other);
// Reset
void clear();
// Accessors
inline T& operator* () const { return *m_ptr; }
inline T* operator-> () const { return m_ptr; }
inline T* get() const { return m_ptr; }
// Operators
COMPARE(==)
COMPARE(!=)
COMPARE(>)
COMPARE(<)
COMPARE(<=)
COMPARE(>=)
private:
//私有成员中生命友元成员,强指针对象sp,和若指针对象wp
template<typename Y> friend class sp;
template<typename Y> friend class wp;
void set_pointer(T* ptr);
T* m_ptr;
};
构造函数
// 普通构造函数
template<typename T>
sp<T>::sp(T* other)
: m_ptr(other) {
if (other)
other->incStrong(this);
}
// 拷贝构造函数
template<typename T>
sp<T>::sp(const sp<T>& other)
: m_ptr(other.m_ptr) {
if (m_ptr)
m_ptr->incStrong(this);
}
构造函数中,由于m_ptr从父类LightRefBase继承下来,这里调用的是LightRefBase的成员函数incStrong()方法实现引用计数的增加。
LightRefBase的析构函数
// 析构函数
template<typename T>
sp<T>::~sp() {
if (m_ptr)
m_ptr->decStrong(this);
}
同样,析构函数中,也是通过m_ptr调用父类的decStrong()实现引用计数的减少。
强指针和弱指针是配合在一起使用的,通过强引用计数和弱引用计数来维护对象的生命周期。其必须继承RefBase类,RefBase类内部提供了强弱指针计数器
StrongPointer
强指针sp实现类
弱指针的实现类和强指针都是一个模版类,具体的定义如下:
–> system/core/include/utils/StrongPointer.h
template<typename T>
class sp {
public:
// 指向实际引用的对象
inline sp() : m_ptr(0) { }
// 4种方式初始化sp对象
sp(T* other);
sp(const sp<T>& other);
template<typename U> sp(U* other);
template<typename U> sp(const sp<U>& other);
~sp();
sp& operator = (T* other);
sp& operator = (const sp<T>& other);
template<typename U> sp& operator = (const sp<U>& other);
template<typename U> sp& operator = (U* other);
void force_set(T* other);
void clear();
// 强指针运算符重载了*、->,可以直接操作对象
inline T& operator* () const { return *m_ptr; }
inline T* operator-> () const { return m_ptr; }
inline T* get() const { return m_ptr; }
// Operators
COMPARE(==)
COMPARE(!=)
COMPARE(>)
COMPARE(<)
COMPARE(<=)
COMPARE(>=)
private:
// 强指针和弱指针sp,wp均是模版类
template<typename Y> friend class sp;
template<typename Y> friend class wp;
void set_pointer(T* ptr);
// 私有成员,指向模版类传入的RefBase子类
T* m_ptr;
};
sp的初始化
sp强引用,内部提供四种初始化方式,方式1,2:调用目标对象的incStrong()方法;方式3,4:则调用目标对象的incStrong()方法,再调用旧对象decStrong()方法
// 方式1,普通构造函数
template<typename T>
sp<T>::sp(T* other)
: m_ptr(other) {
if (other)
other->incStrong(this);
}
// 方式2,拷贝构造函数
template<typename T>
sp<T>::sp(const sp<T>& other)
: m_ptr(other.m_ptr) {
if (m_ptr)
m_ptr->incStrong(this);
}
// 方式3
template<typename T> template<typename U>
sp<T>::sp(U* other)
: m_ptr(other) {
if (other)
((T*) other)->incStrong(this);
}
// 方式4
template<typename T> template<typename U>
sp<T>::sp(const sp<U>& other)
: m_ptr(other.m_ptr) {
if (m_ptr)
m_ptr->incStrong(this);
}
具体实现见下面的分析。
弱指针wp实现
弱指针实现相比强指针实现要复杂,强弱指针都是配合使用。
–> /system/core/include/utils/RefBase.h
template <typename T>
class wp
{
public:
typedef typename RefBase::weakref_type weakref_type;
// 构造函数
inline wp() : m_ptr(0) { }
// 提供6中初始化方式
wp(T* other);
wp(const wp<T>& other);
wp(const sp<T>& other);
template<typename U> wp(U* other);
template<typename U> wp(const sp<U>& other);
template<typename U> wp(const wp<U>& other);
~wp();
// Assignment
wp& operator = (T* other);
wp& operator = (const wp<T>& other);
wp& operator = (const sp<T>& other);
template<typename U> wp& operator = (U* other);
template<typename U> wp& operator = (const wp<U>& other);
template<typename U> wp& operator = (const sp<U>& other);
void set_object_and_refs(T* other, weakref_type* refs);
// 升级弱指针至强指针
sp<T> promote() const;
// 重置
void clear();
// Accessors
inline weakref_type* get_refs() const { return m_refs; }
inline T* unsafe_get() const { return m_ptr; }
// Operators
COMPARE_WEAK(==)
COMPARE_WEAK(!=)
COMPARE_WEAK(>)
COMPARE_WEAK(<)
COMPARE_WEAK(<=)
COMPARE_WEAK(>=)
// 运算符重载
inline bool operator == (const wp<T>& o) const {
return (m_ptr == o.m_ptr) && (m_refs == o.m_refs);
}
template<typename U>
inline bool operator == (const wp<U>& o) const {
return m_ptr == o.m_ptr;
}
...
private:
template<typename Y> friend class sp;
template<typename Y> friend class wp;
T* m_ptr;// 指向引用对象
weakref_type* m_refs;// 维护对象的弱引用计数器
};
具体的6种初始化方式
template<typename T>
wp<T>::wp(T* other)
: m_ptr(other)
{
if (other) m_refs = other->createWeak(this);
}
template<typename T>
wp<T>::wp(const wp<T>& other)
: m_ptr(other.m_ptr), m_refs(other.m_refs)
{
if (m_ptr) m_refs->incWeak(this);
}
template<typename T>
wp<T>::wp(const sp<T>& other)
: m_ptr(other.m_ptr)
{
if (m_ptr) {
m_refs = m_ptr->createWeak(this);
}
}
template<typename T> template<typename U>
wp<T>::wp(U* other)
: m_ptr(other)
{
if (other) m_refs = other->createWeak(this);
}
template<typename T> template<typename U>
wp<T>::wp(const wp<U>& other)
: m_ptr(other.m_ptr)
{
if (m_ptr) {
m_refs = other.m_refs;
m_refs->incWeak(this);
}
}
template<typename T> template<typename U>
wp<T>::wp(const sp<U>& other)
: m_ptr(other.m_ptr)
{
if (m_ptr) {
m_refs = m_ptr->createWeak(this);
}
}
无论哪种方式,最终走到incWeak,增加实际引用对象的弱引用计数
void RefBase::weakref_type::incWeak(const void* id)
{
// 转为实现类weakref_impl来创建弱引用
weakref_impl* const impl = static_cast<weakref_impl*>(this);
impl->addWeakRef(id);
const int32_t c __unused = android_atomic_inc(&impl->mWeak);
ALOG_ASSERT(c >= 0, "incWeak called on %p after last weak ref", this);
}
具体实现如下:
void addWeakRef(const void* id) {
addRef(&mWeakRefs, id, mWeak);
}
void addRef(ref_entry** refs, const void* id, int32_t mRef)
{
if (mTrackEnabled) {
AutoMutex _l(mMutex);
ref_entry* ref = new ref_entry;
ref->ref = mRef;
ref->id = id;
ref->next = *refs;
*refs = ref;
}
}
弱引用和强引用最大的区别是弱引用不能直接操作对象,因为它所引用的可能是不受弱引用计数控制的,即可能是一个无效对象。如果需要操作弱引用对象,必须调用promote方法要将其升级成强引用才能操作,但是不一定能升级成功。
再看RefBase
RefBase内部声明了了强弱指针的基本逻辑,具体代码如下:
class RefBase
{
public:
// 强引用计数的增减操作
void incStrong(const void* id) const;
void decStrong(const void* id) const;
void forceIncStrong(const void* id) const;
//! DEBUGGING ONLY: Get current strong ref count.
int32_t getStrongCount() const;
// 内部类,弱引用的相关操作
class weakref_type
{
public:
RefBase* refBase() const;
void incWeak(const void* id);
void decWeak(const void* id);
bool attemptIncStrong(const void* id);
bool attemptIncWeak(const void* id);
int32_t getWeakCount() const;
void printRefs() const;
void trackMe(bool enable, bool retain);
};
weakref_type* createWeak(const void* id) const;
weakref_type* getWeakRefs() const;
inline void printRefs() const { getWeakRefs()->printRefs(); }
inline void trackMe(bool enable, bool retain)
{
getWeakRefs()->trackMe(enable, retain);
}
typedef RefBase basetype;
protected:
RefBase();
virtual ~RefBase();
//! Flags for extendObjectLifetime()
// 生命周期的控制方式
enum {
OBJECT_LIFETIME_STRONG = 0x0000,
OBJECT_LIFETIME_WEAK = 0x0001,
OBJECT_LIFETIME_MASK = 0x0001
};
void extendObjectLifetime(int32_t mode);
//! Flags for onIncStrongAttempted()
// 强引用计数值的默认值
enum {
FIRST_INC_STRONG = 0x0001
};
// 根据引用的计数值的改变回调相应方法
virtual void onFirstRef();
virtual void onLastStrongRef(const void* id);
virtual bool onIncStrongAttempted(uint32_t flags, const void* id);
virtual void onLastWeakRef(const void* id);
private:
friend class weakref_type;
class weakref_impl;
RefBase(const RefBase& o);
RefBase& operator=(const RefBase& o);
private:
friend class ReferenceMover;
static void renameRefs(size_t n, const ReferenceRenamer& renamer);
static void renameRefId(weakref_type* ref,
const void* old_id, const void* new_id);
static void renameRefId(RefBase* ref,
const void* old_id, const void* new_id);
// weakref_type的实现类
weakref_impl* const mRefs;
};
- RefBase内部可以直接操作强引用计数,实现增加和减少引用
- 对于弱引用,则通过内部类 weakref_type 的内部成员refBase,间接调用内部类的方法实现引用计数的增减,后续分析会讲到
- 为了方便操作弱引用对象,内部类提供升级弱引用到强引用的方法,但需要结合特定条件,不一定升级成功
- 私有成员weakref_impl实现weakref_type方法,后续讲到
- 生命周期的控制方式
OBJECT_LIFETIME_STRONG 强引用计数控制
OBJECT_LIFETIME_WEAK 强弱引用计数控制
OBJECT_LIFETIME_FOREVER 完全无视(4.4后弃用)
这里引用Gityuan博客内的UML类图来说明一下
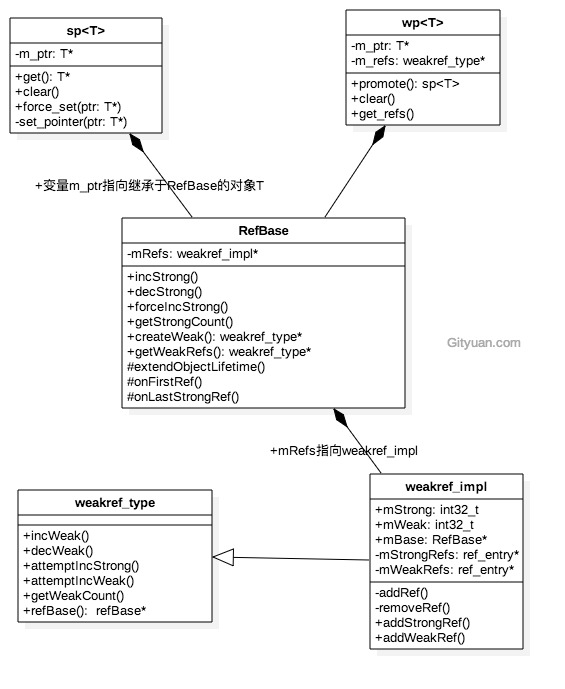
weakref_imp的实现
weakref_imp继承于weakref_type,是其具体逻辑的实现类
class RefBase::weakref_impl : public RefBase::weakref_type
{
public:
volatile int32_t mStrong;// 强引用值
volatile int32_t mWeak;// 弱引用值
RefBase* const mBase;// 指向父类的RefBase
volatile int32_t mFlags;// 对象声明周期控制方式
// 通过初始化列表初始化相应的值
weakref_impl(RefBase* base)
: mStrong(INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE)
, mWeak(0)
, mBase(base)
, mFlags(0)
, mStrongRefs(NULL)
, mWeakRefs(NULL)
, mTrackEnabled(!!DEBUG_REFS_ENABLED_BY_DEFAULT)
, mRetain(false)
{
}
// 析构函数实现
~weakref_impl()
{
bool dumpStack = false;
if (!mRetain && mStrongRefs != NULL) {
dumpStack = true;
ALOGE("Strong references remain:");
ref_entry* refs = mStrongRefs;
while (refs) {
char inc = refs->ref >= 0 ? '+' : '-';
ALOGD("\t%c ID %p (ref %d):", inc, refs->id, refs->ref);
refs = refs->next;
}
}
if (!mRetain && mWeakRefs != NULL) {
dumpStack = true;
ALOGE("Weak references remain!");
ref_entry* refs = mWeakRefs;
while (refs) {
char inc = refs->ref >= 0 ? '+' : '-';
ALOGD("\t%c ID %p (ref %d):", inc, refs->id, refs->ref);
refs = refs->next;
}
}
if (dumpStack) {
ALOGE("above errors at:");
CallStack stack(LOG_TAG);
}
}
...
};
weakref_imp实现了weakref_type内部的若干方法,其内部相关变量维持对象引用的相关信息,具体的实现过程见下分析。
INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE (1<<28),至于初始值不为0后续会分析得到。
引用计数的增减逻辑
强引用计数增加逻辑incStrong
void RefBase::incStrong(const void* id) const
{
weakref_impl* const refs = mRefs;
refs->incWeak(id);
refs->addStrongRef(id);
const int32_t c = android_atomic_inc(&refs->mStrong);
ALOG_ASSERT(c > 0, "incStrong() called on %p after last strong ref", refs);
if (c != INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE) {
return;
}
android_atomic_add(-INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE, &refs->mStrong);
refs->mBase->onFirstRef();
}
mRefs为RefBase的成员变量,在RefBase的构造函数中实现
RefBase::RefBase()
: mRefs(new weakref_impl(this)){}
mRefs的类型为weakref_impl,incStrong增加强引用计数实际上是调用weakref_impl的具体方法实现的
- 增加弱引用计数
- 增加强引用计数
- 原子层实现mStrong的值增加,返回先前值
- 根据返回值c,如果是首次增加即c=INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE,那么回调引用对象mBase(RefBase的引用)的onFirstRef方法,子类可以自己实现一些首次绑定的相关逻辑
这里可以看出初始化值INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE的作用了,因为需要判断一个状态就是强引用计数有没有被使用过,如果用0的话,那么就不能区分0值代表是没使用过,还是使用过了清零了,所以这里不用0来做初始化值。
void RefBase::weakref_type::incWeak(const void* id)
{
weakref_impl* const impl = static_cast<weakref_impl*>(this);
impl->addWeakRef(id);
const int32_t c __unused = android_atomic_inc(&impl->mWeak);
ALOG_ASSERT(c >= 0, "incWeak called on %p after last weak ref", this);
}
弱引用计数的增加,同样是通过weakref_impl实现类addWeakRef来实现,在原子层实现。同时,weakref_impl在声明时,即对addWeakRef实现了具体的方法,通过传入mWeakRefs,mWeakRefs是弱引用计数值的引用。
void addWeakRef(const void* id) {
addRef(&mWeakRefs, id, mWeak);
}
void addRef(ref_entry** refs, const void* id, int32_t mRef)
{
if (mTrackEnabled) {
AutoMutex _l(mMutex);
ref_entry* ref = new ref_entry;
// Reference count at the time of the snapshot, but before the
// update. Positive value means we increment, negative--we
// decrement the reference count.
ref->ref = mRef;
ref->id = id;
ref->next = *refs;
*refs = ref;
}
}
addStrongRef也是通过实现类weakref_impl来实现的,这里传入的值为mStrongRefs,实现方法同上面的addRef
void addStrongRef(const void* id) {
addRef(&mStrongRefs, id, mStrong);
}
减少强引用计数逻辑decStrong
void RefBase::decStrong(const void* id) const
{
weakref_impl* const refs = mRefs;
refs->removeStrongRef(id);
const int32_t c = android_atomic_dec(&refs->mStrong);
if (c == 1) {
refs->mBase->onLastStrongRef(id);
// 周期控制方式为强引用控制方式,无引用即删除对象,释放内存
if ((refs->mFlags&OBJECT_LIFETIME_MASK) == OBJECT_LIFETIME_STRONG) {
delete this;
}
}
refs->decWeak(id);
}
强引用计数的减少,流程如下:
- 通过实现类weakref_impl,首先减少强引用计数
- 如果强引用计数为0(无引用),回调onLastStrongRef方法,子类可以在删除对象前实现自定的逻辑
- 根据对象的生命周期控制方式,删除对象,释放内存
- 减少弱引用对象引用计数
首先减少对应的强引用计数
void removeStrongRef(const void* id) {
if (!mRetain) {
removeRef(&mStrongRefs, id);
} else {
addRef(&mStrongRefs, id, -mStrong);
}
}
mRetain初始化是默认值false,通过传入的mStrongRefs引用值,实现值的减少。
void removeRef(ref_entry** refs, const void* id)
{
if (mTrackEnabled) {
AutoMutex _l(mMutex);
ref_entry* const head = *refs;
ref_entry* ref = head;
while (ref != NULL) {
if (ref->id == id) {
*refs = ref->next;
delete ref;
return;
}
refs = &ref->next;
ref = *refs;
}
ref = head;
while (ref) {
char inc = ref->ref >= 0 ? '+' : '-';
ALOGD("\t%c ID %p (ref %d):", inc, ref->id, ref->ref);
ref = ref->next;
}
CallStack stack(LOG_TAG);
}
}
再减少弱引用计数
void RefBase::weakref_type::decWeak(const void* id)
{
weakref_impl* const impl = static_cast<weakref_impl*>(this);
impl->removeWeakRef(id);
const int32_t c = android_atomic_dec(&impl->mWeak);
// 回传先前c值,如果c=1,代表此时不存在弱引用对应了,需要具体判断处理
if (c != 1) return;
if ((impl->mFlags&OBJECT_LIFETIME_WEAK) == OBJECT_LIFETIME_STRONG) {
if (impl->mStrong == INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE) {
delete impl->mBase;
} else {
delete impl;
}
} else {
impl->mBase->onLastWeakRef(id);
if ((impl->mFlags&OBJECT_LIFETIME_MASK) == OBJECT_LIFETIME_WEAK) {
delete impl->mBase;
}
}
}
根据代码可以看出,如果此时减少弱引用计数,如果不存在引用对象,需要具体操作,否则操作完直接返回。
生命周期控制方式为强引用情况下:
1. 强引用计数值为恢复初始状态,从未被强引用引用过,此时弱引用又为0,可以删除对象了。
2. 对象生命周期受强引用计数控制,被强引用过,现在弱引用为0(强引用之前也必定为0),也就是说,对象已经在decStrong中释放掉了,这里需要释放内部的引用计数器实现类weakref_impl
其次,如果是受其他方式控制,弱引用计数值为0时
1. 回调RefBase的onLastWeakRef方法,子类实现弱引用删除前的一些自定操作,
2. 控制方式为弱引用方式,删除对象
小结强引用
- 如果对象声明周期只受强引用控制,如果强引用计数值为0,系统自动释放这个对象
- 如果对象生命周期只受弱引用控制,只有当强引用值和弱引用值都为0时,系统才会释放这个对象
- 系统释放对象前,会回调一些方法由子类实现自定逻辑
析构过程
sp析构过程
模版类sp通过RefBase类m_ptr调用decStrong方法
template<typename T> sp<T>::~sp() { if (m_ptr) m_ptr->decStrong(this); }sp析构过程,调用RefBase的decStrong实现
void RefBase::decStrong(const void* id) const { weakref_impl* const refs = mRefs; refs->removeStrongRef(id); const int32_t c = android_atomic_dec(&refs->mStrong); ALOG_ASSERT(c >= 1, "decStrong() called on %p too many times", refs); if (c == 1) { refs->mBase->onLastStrongRef(id); if ((refs->mFlags&OBJECT_LIFETIME_MASK) == OBJECT_LIFETIME_STRONG) { delete this; } } // 减少弱引用 refs->decWeak(id); }
wp析构过程
模版类wp
template<typename T> wp<T>::~wp() { if (m_ptr) m_refs->decWeak(this); }弱引用wp的析构过程调用RefBase内部类weakref_type的decWeak实现
void RefBase::weakref_type::decWeak(const void* id) { weakref_impl* const impl = static_cast<weakref_impl*>(this); impl->removeWeakRef(id); const int32_t c = android_atomic_dec(&impl->mWeak); ALOG_ASSERT(c >= 1, "decWeak called on %p too many times", this); if (c != 1) return; if ((impl->mFlags&OBJECT_LIFETIME_WEAK) == OBJECT_LIFETIME_STRONG) { if (impl->mStrong == INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE) { delete impl->mBase; } else { delete impl; } } else { impl->mBase->onLastWeakRef(id); if ((impl->mFlags&OBJECT_LIFETIME_MASK) == OBJECT_LIFETIME_WEAK) { delete impl->mBase; } } }
RefBase析构过程
RefBase析构过程涉及到其内部引用对象的减少以及释放,其过程涉及到sp和wp的析构过程,具体实现如下:
RefBase::~RefBase()
{
// 释放weakref_impl对象
if (mRefs->mStrong == INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE) {
delete mRefs;
} else {
// 非STRONG模式下,弱引用计数为0,则释放weakref_impl对象
if ((mRefs->mFlags & OBJECT_LIFETIME_MASK) != OBJECT_LIFETIME_STRONG) {
if (mRefs->mWeak == 0) {
delete mRefs;
}
}
}
const_cast<weakref_impl*&>(mRefs) = NULL;
}
decStrong执行强指针sp的析构过程
void RefBase::decStrong(const void* id) const
{
weakref_impl* const refs = mRefs;
refs->removeStrongRef(id);
const int32_t c = android_atomic_dec(&refs->mStrong);
ALOG_ASSERT(c >= 1, "decStrong() called on %p too many times", refs);
if (c == 1) {
refs->mBase->onLastStrongRef(id);
if ((refs->mFlags&OBJECT_LIFETIME_MASK) == OBJECT_LIFETIME_STRONG) {
delete this;
}
}
refs->decWeak(id);
}
总结decStrong逻辑如下:
- 减少对应的强引用计数值
- 强引用计数为0,回调onLastStrongRef方法
- 无引用且生命周期控制方式为强引用,删除对象操作
- 减少弱引用计数值
decWeak的具体实现
decWeak执行了弱指针wp的析构过程
void RefBase::weakref_type::decWeak(const void* id)
{
weakref_impl* const impl = static_cast<weakref_impl*>(this);
impl->removeWeakRef(id);
const int32_t c = android_atomic_dec(&impl->mWeak);
ALOG_ASSERT(c >= 1, "decWeak called on %p too many times", this);
if (c != 1) return;
if ((impl->mFlags&OBJECT_LIFETIME_WEAK) == OBJECT_LIFETIME_STRONG) {
if (impl->mStrong == INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE) {
delete impl->mBase;
} else {
delete impl;
}
} else {
impl->mBase->onLastWeakRef(id);
if ((impl->mFlags&OBJECT_LIFETIME_MASK) == OBJECT_LIFETIME_WEAK) {
delete impl->mBase;
}
}
}
总结decWeak逻辑如下:
- 减少对应的弱引用计数
- 如果弱引用计数为0(相应的强引用计数值肯定为0),根据情况决定操作:
- 强引用控制方式情况下:
- 强引用计数值为初始化的默认值,弱引用计数值为0,释放引用对象
- 其他情况,强引用计数值为0,在decStrong释放对象内存,这里弱引用也为0,释放内部的引用计数器weakref_impl对象
- 其他控制方式
- 回调onLastWeakRef,子类自定实现逻辑
- 若果是弱引用控制方式,删除对象引用
- 强引用控制方式情况下:
这样,在RefBase完成析构过程中,就完成了其内部关联的强引用、弱引用对象的减少以及必要的对象的内存释放,当然具体的逻辑需要看对象生命周期的控制方式。
弱指针升级过程分析
弱指针如果想要操作引用对象,需要通过promote方法将弱指针升级到强指针,因为涉及到引用对象生命周期控制方式以及对象的存在与否,逻辑相对复杂。
promote升级指针
promote,弱指针内部声明了promote()方法,其具体实现如下:
template<typename T>
sp<T> wp<T>::promote() const
{
sp<T> result;
if (m_ptr && m_refs->attemptIncStrong(&result)) {
result.set_pointer(m_ptr);
}
return result;
}
m_ptr指向引用对象的地址,只有m_ptr不为NULL,执行m_refs->attemptIncStrong(&result)方法
attemptIncStrong 尝试增减引用计数
bool RefBase::weakref_type::attemptIncStrong(const void* id)
{
// 首先增加对应的弱引用计数
incWeak(id);
// 转为weakref_impl获取强引用计数值
weakref_impl* const impl = static_cast<weakref_impl*>(this);
int32_t curCount = impl->mStrong;
ALOG_ASSERT(curCount >= 0,
"attemptIncStrong called on %p after underflow", this);
// 强引用计数大于0,且初始化过(不是默认值),对象肯定存在
while (curCount > 0 && curCount != INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE) {
// 此弱引用对象存在强引用,可以升级,成功返回0
if (android_atomic_cmpxchg(curCount, curCount+1, &impl->mStrong) == 0) {
break;
}
curCount = impl->mStrong;
}
// 弱引用对象的强引用计数值小于等于0(存在)或者初始化值为默认值(不存在)
if (curCount <= 0 || curCount == INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE) {
// 生命周期受强引用计数控制
if ((impl->mFlags&OBJECT_LIFETIME_WEAK) == OBJECT_LIFETIME_STRONG) {
// 引用对象的强引用计数值小于等0,不存在了
if (curCount <= 0) {
// 减少之前增加的弱引用计数值,升级失败
decWeak(id);
return false;
}
// 这种条件下,引用对象计数值为默认值,又因为只受强引用控制,肯定存在可以升级
while (curCount > 0) {
// 因为原子性操作问题,循环操作升级逻辑
if (android_atomic_cmpxchg(curCount, curCount + 1,
&impl->mStrong) == 0) {
break;
}
curCount = impl->mStrong;
}
// 升级后引用值还是小于等于0,升级失败,执行减少之前弱引用计数值操作
if (curCount <= 0) {
decWeak(id);
return false;
}
} else {
// 判断对象是否允许强指针引用它
if (!impl->mBase->onIncStrongAttempted(FIRST_INC_STRONG, id)) {
// 不允许,减少之前的弱引用计数,升级失败
decWeak(id);
return false;
}
// 权限通过,执行升级操作
curCount = android_atomic_inc(&impl->mStrong);
}
// 已经被强指针引用了,还要升级!此时onLastStrongRef持有了无用的引用,这里调用并释放它。注意确保这不是第一次引用的情况
if (curCount > 0 && curCount < INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE) {
impl->mBase->onLastStrongRef(id);
}
}
impl->addStrongRef(id);
curCount = impl->mStrong;
// 由于初始化的强引用计数值不是0,这里需要矫正强引用计数值
while (curCount >= INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE) {
ALOG_ASSERT(curCount > INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE,
"attemptIncStrong in %p underflowed to INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE",
this);
if (android_atomic_cmpxchg(curCount, curCount-INITIAL_STRONG_VALUE,
&impl->mStrong) == 0) {
break;
}
curCount = impl->mStrong;
}
// 升级成功
return true;
}
这里的逻辑在代码中已经有相关的注释,总结一下弱指针升级强指针的流程:
- 强指针引用的增加必然导致弱引用的增加,因此首先增加弱引用计数值
- 获取引用对象的强引用计数值
- 强引用计数值大于0且初始化过,对象一定存在,直接升级,并增加强引用计数值
- 升级失败,减少之前弱引用计数值,返回升级失败
- 其他条件下:
- 对象受强引用控制,且强引用计数值小于等于0,对象不存在,无法升级,执行升级失败操作,减少开始弱引用计数值,升级失败,直接返回
- 受强引用控制,且对象强引用计数值为初始值,对象肯定存在,多线程下循环升级保持原子性
- 检查步骤2升级是否成功,失败便执行上述升级失败操作
- 对象不受强引用控制,判断是否允许强指针引用它,不通过,执行实际失败操作;权限通过便执行升级
- 最后,判断如下情况:对象已经被强指针引用了,还要升级!此时onLastStrongRef持有了无用的引用,这里调用并释放它。注意确保不是首次强引用的情况下!
- 由于初始化的强引用计数值不是0,这里需要在结尾处矫正强引用计数值
- 返回升级结果,升级成功
到此,弱指针升级到强指针的逻辑就分析完毕了,升级后的强引用对象可以直接操作的,愿意就是强指针内部重载了对应的操作符。
总结
强弱引用关系
- 对象通过extendObjectLifetime()方法设置生命后期的控制方式
- 引用对象生命周期无论受强引用还是弱引用控制,弱引用计数始终大于等于强引用
- 强引用控制情况下:强引用值的增减都和弱引用值同步,且强引用计数值为0便删除引用对象,与弱引用值无关,弱引用计数此时控制weakref_impl的生命周期
- 弱引用控制情况下:弱引用计数值为0才进行对象的删除,同时删除weakref_impl对象
RefBase的方法回调时机
- 首次调用对象incStrong(),回调该对象的onFirstRef().
- 调用decStrong()的最后一次,回调该对象的onLastStrongRef()
- 调用decWeak()的最后一次,回调对象的onLastWeakRef()
相关说明
参考书籍:Android系统源代码情景分析

